Purified meta-Cresol Purple dye perturbation: How it influences spectrophotometric power of hydrogen measurements
Journal: Marine Chemistry (2020)
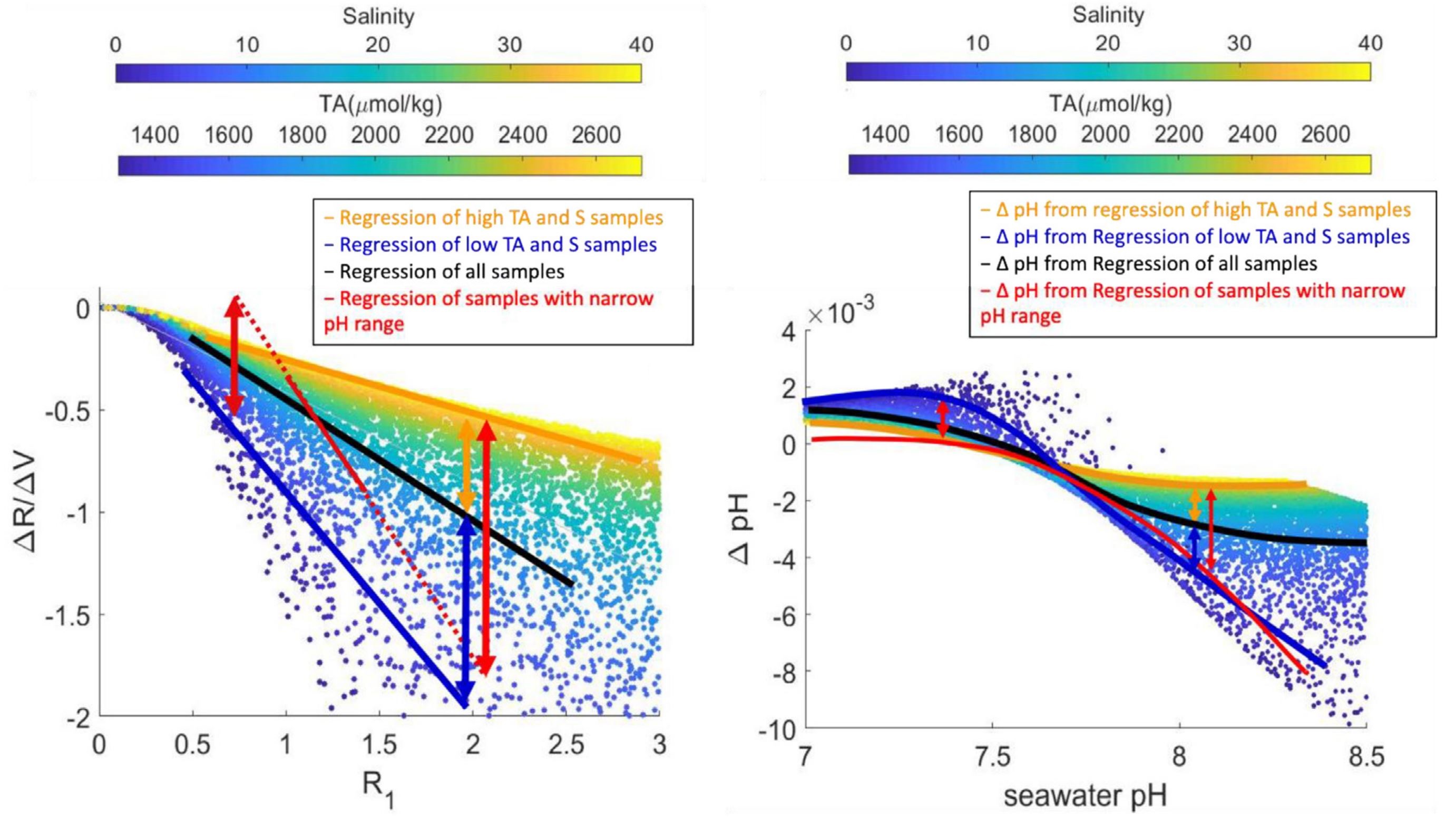
Ocean acidification, a phenomenon of seawater pH decreasing due to increasing atmospheric CO₂, has a global effect on seawater chemistry, marine biology, and ecosystems. Ocean acidification is a gradual and global long-term process, the study of which demands high-quality pH data. The spectrophotometric technique is capable of generating accurate and precise pH measurements but requires adding an indicator dye that perturbs the sample original pH. While the perturbation is modest in well-buffered seawater, applications of the method in environments with lower buffer capacity such as riverine, estuarine, sea-ice meltwater and lacustrine environments are increasingly common, and uncertainties related to larger potential dye perturbations need further evaluation. In this paper, we assess the effect of purified meta-Cresol Purple (mCP) dye addition on the sample pH and how to correct for this dye perturbation. We conducted numerical simulations by incorporating mCP speciation into the MATLAB CO2SYS program to examine the changes in water sample pH caused by the dye addition and to reveal the dye perturbation mechanisms. Then, laboratory experiments were carried out to verify the simulation results. The simulations suggest that the dye perturbation on sample pH is a result of total alkalinity (TA) contributions from the indicator dye and chemical equilibrium shifts that are related to both the water sample properties (pH, TA, and salinity) and the indicator dye solution properties (pH and solvent matrix). The laboratory experiments supported the simulation results; the same dye solution can lead to different dye perturbations in water samples with different pH, TA, and salinity values. The modeled adjustments agreed well with the empirically determined adjustments for salinities >5, but it showed greater errors for lower salinities with disagreements as large as 0.005 pH units. Adjustments are minimized when the pH and salinity of the dye are matched to the sample. When the dye is used over a wide range of salinity, we suggest that it should be prepared in deionized water to minimize the dye perturbation effect on pH in the fresher sample waters with less well-constrained perturbation adjustments. We also suggest that the dye perturbation correction should be based on double dye addition experiments performed over a wide range of pH, TA, and salinity. Otherwise, multiple volume dye addition experiments are recommended for each sample to determine the dye perturbation adjustment. We further create a MATLAB function dyeperturbation.m that calculates the expected dye perturbation. This function can be used to validate empirically-derived adjustments or in lieu of empirical adjustments if dye addition experiments are unfeasible (e.g., for historical data). This study of dye perturbation evaluation and correction will improve the accuracy of the pH data, necessary for monitoring the long-term anthropogenic-driven changes in the seawater carbonate system.